Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Digital Circuit Design. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast, a student, or a professional engineer, understanding digital circuit design is crucial in today’s technology-driven world. Digital circuits form the backbone of modern electronics, powering everything from smartphones to advanced computing systems. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of digital circuits, provide real-life examples, delve into the differences between analog and digital designs, and highlight the latest advancements in the field. Let’s embark on this electrifying journey into the world of digital electronics!

What is Digital Circuit Design?
At its core, Digital Circuit Design involves creating electronic circuits that process digital signals—those represented by binary digits, ‘0’ and ‘1’. Unlike analog circuits, which handle continuously varying signals, digital circuits operate with discrete levels, making them more reliable and easier to design for complex functionalities. This distinction is akin to having a light switch that is either on or off, rather than one that can be dimmed to any brightness level.
In modern applications, digital circuits are ubiquitous. From controlling household appliances and managing automotive systems to powering intricate medical devices and enabling high-speed communication networks, digital circuits are everywhere. Their ability to perform precise operations with minimal error makes them indispensable in today’s electronic landscape.
Examples of Digital Circuits
Digital circuits are integral to a myriad of everyday devices and advanced technologies. Here are some notable examples:
- Computers and Smartphones: These devices rely on complex digital circuits to perform computations, manage data, and run applications efficiently.
- Digital Watches and Clocks: Timekeeping in these devices is managed by digital circuits that ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Automotive Systems: Modern vehicles use digital circuits for engine control units (ECUs), anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and infotainment systems.
- Medical Equipment: Devices like MRI machines, digital thermometers, and insulin pumps utilize digital circuits for precise measurements and operations.
- Home Appliances: From washing machines to smart refrigerators, digital circuits enhance functionality and efficiency.

Analog and Digital Circuit Design
Understanding the distinction between analog and digital circuits is fundamental to grasping digital circuit design:
Analog Circuit Design
Analog circuits deal with continuously varying signals. These signals can represent real-world phenomena like sound, light, temperature, and pressure. For instance, a microphone converts sound waves into electrical signals that vary in amplitude and frequency—characteristics that are inherently analog.

Consider a CD player: it uses optical components to read digital data from a disk, which is then converted into analog signals through a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) before being amplified and sent to speakers. This seamless transition between digital data and analog output highlights the interplay between the two types of circuit designs.
Digital Integrated Circuits
Most modern digital systems utilize Digital Integrated Circuits (ICs), which integrate multiple electronic components into a single chip. This integration offers numerous benefits, including reduced size, lower power consumption, and enhanced performance. ICs come in various fabrication technologies, each tailored to specific applications:
- TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic): Uses bipolar junction transistors and is known for its speed and reliability.
- CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): Utilizes MOSFETs and is prized for its low power consumption and high noise immunity.
- ECL (Emitter-Coupled Logic): Offers the fastest switching speeds but consumes more power.
- BiCMOS: Combines the advantages of both Bipolar and CMOS technologies, balancing speed and power efficiency.
Logic Gates
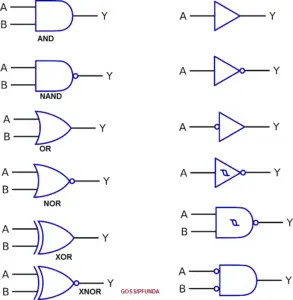
Logic gates are the fundamental building blocks of digital circuits. Each gate performs a basic logical function based on its inputs:
- Inverter (NOT Gate): Outputs the opposite of the input.
- AND Gate: Outputs ‘1’ only if all inputs are ‘1’.
- OR Gate: Outputs ‘1’ if at least one input is ‘1’.
- NAND Gate: Outputs the opposite of the AND gate.
- NOR Gate: Outputs the opposite of the OR gate.
- Exclusive-OR (XOR) Gate: Outputs ‘1’ if an odd number of inputs are ‘1’.
- Exclusive-NOR (XNOR) Gate: Outputs ‘1’ if an even number of inputs are ‘1’.
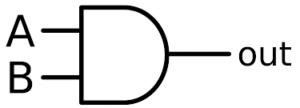
While the basic gates handle simple operations, NAND and NOR gates are particularly powerful as they are known as universal gates. This means any logical function can be implemented using just NAND or NOR gates, offering flexibility in circuit design. To delve deeper, explore our resources on how transistors work.
Logic Families

Over the years, various logic families have been developed, each with distinct characteristics and applications:
- RTL (Resistor-Transistor Logic): The earliest logic family, now largely obsolete due to its high power consumption.
- DTL (Diode-Transistor Logic): Improved upon RTL by introducing diodes, offering better performance.
- TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic): Known for its speed and reliability, widely used in digital systems.
- Schottky TTL: A variant of TTL with faster switching speeds.
- ECL (Emitter-Coupled Logic): The fastest logic family, ideal for high-speed applications but consumes more power.
- I2L (Integrated-Injection Logic): Utilizes bipolar junction transistors, suitable for high-density integrations.
- CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor): Dominates modern electronics due to its low power consumption and high noise immunity.
VLSI Basics

Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) refers to the process of integrating thousands to millions of transistors into a single chip. Originating in the early 1970s, VLSI technology has been pivotal in advancing microprocessors, memory chips, and various digital systems. By enabling higher transistor densities, VLSI allows for more complex and powerful electronic devices.
ULSI Basics

Ultra-Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) takes VLSI a step further by integrating millions of transistors on a single chip. This advancement has facilitated the development of highly sophisticated microprocessors and system-on-chip (SoC) designs, which are essential for modern computing devices and applications.
GSI Basics

Gigascale Integration (GSI) is the latest frontier in integrated circuit technology, integrating billions of transistors on a single chip. GSI is crucial for cutting-edge applications like artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and advanced telecommunications. Techniques such as multi-core processing and 3D stacking are commonly employed to achieve the densities required for GSI.
Difference between Analog and Digital Computer
Analog Computer
Analog computers process data represented by continuously varying physical quantities like voltage, current, or mechanical motion. These computers excel in modeling and solving differential equations, making them ideal for applications in engineering and scientific simulations.
For example, an analog computer can simulate the behavior of a spring-mass-damper system, providing real-time visualization of its dynamics. However, analog computers are limited by their lack of versatility and precision, as they are susceptible to noise and component variations.
Advantages
Analog computers offer several benefits:
- Real-Time Processing: Capable of processing data in real-time without the need for digital conversion.
- High-Speed Calculations: Efficient in solving differential equations and simulating dynamic systems quickly.
- Simple Hardware: Requires fewer components for certain types of calculations compared to digital systems.
Disadvantages
Despite their advantages, analog computers have notable limitations:
- Low Precision: Susceptible to noise and component tolerances, leading to inaccuracies.
- Lack of Flexibility: Primarily designed for specific tasks, making them less versatile than digital computers.
- Complex Calibration: Requires careful calibration to maintain accuracy, which can be time-consuming.
Digital Computer
Digital computers operate using binary digits (‘0’ and ‘1’), representing discrete values. They are highly versatile, programmable, and capable of performing a wide range of tasks with high precision. Modern digital computers power everything from personal laptops and smartphones to large-scale servers and supercomputers.
Digital computers offer several advantages over their analog counterparts:
- High Precision: Capable of performing calculations with exact values, minimizing errors.
- Flexibility: Programmable to handle a vast array of applications and tasks.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces and software make digital computers accessible to a wide audience.
- Scalability: Can be scaled from simple microcontrollers to complex multi-core processors.
However, digital computers also come with their own set of considerations:
- Power Consumption: High-performance digital circuits can consume significant power.
- Heat Dissipation: Increased power consumption leads to more heat, necessitating effective cooling solutions.
- Complexity: Designing and manufacturing advanced digital circuits requires sophisticated techniques and equipment.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve delved into the essentials of Digital Circuit Design, exploring its fundamentals, real-life applications, and the critical differences between analog and digital systems. Understanding logic gates, logic families, and the various scales of integration—from VLSI to GSI—provides a solid foundation for anyone interested in electronics and digital systems. As technology continues to advance, the role of digital circuits becomes increasingly pivotal, driving innovations in numerous fields. Stay updated with the latest trends and deepen your knowledge by visiting Gossipfunda for more insightful articles and resources on digital electronics and beyond.
Awill Guru is a technology enthusiast with degrees in VLSI Engineering (B.Tech, M.Tech) and Android Development. Their passion for education drives them to teach and share knowledge through their blog. He also hold qualifications in Sociology (M.A.) and Education (B.Ed), along with NIELIT O and A Level certifications.


